Threat Intelligence Blog

Contact us to discuss any insights from our Blog, and how we can support you in a tailored threat intelligence report.
Black Arrow Cyber Threat Briefing 10 March 2023
Black Arrow Cyber Threat Briefing 10 March 2023:
-Business Email Compromise Attacks Can Take Just Hours
-Research Reveals ‘Password’ is Still the Most Common Term used by Hackers to Breach Enterprise Networks
-Just 10% of Firms Can Resolve Cloud Threats in an Hour
-MSPs in the Crosshair of Ransomware Gangs
-Stolen Credentials Increasingly Empower the Cyber Crime Underground
-It’s Time to Assess the Potential Dangers of an Increasingly Connected World
-Mounting Cyber Threats Mean Financial Firms Urgently Need Better Safeguards
-Developers Leaked 10m Credentials Including Passwords in 2022
-Cyber Threat Detections Surges 55% In 2022
-European Central Bank Tells Banks to Run Cyber Stress Tests after Rise in Hacker Attacks
-Employees Are Feeding Sensitive Business Data to ChatGPT
-Is Ransomware Declining? Not So Fast Experts Say
-Preventing Corporate Data Breaches Starts With Remembering That Leaks Have Real Victims
-Faced With Likelihood of Ransomware Attacks, Businesses Still Choosing to Pay Up
-Experts See Growing Need for Cyber Security Workers as One in Six Jobs go Unfilled
Welcome to this week’s Black Arrow Cyber Threat Briefing – a weekly digest, collated and curated by our cyber threat intelligence experts to provide senior and middle management with an easy to digest round up of the most notable threats, vulnerabilities, and cyber related news from the last week.
Top Cyber Stories of the Last Week
Business Email Compromise Attacks Can Take Just Hours
Microsoft’s security intelligence team found that Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks are moving rapidly, with some taking mere minutes. Microsoft found the whole process, from signing in using compromised credentials to registering typo squatting domains and hijacking an email thread, took threat actors only a couple of hours. Such a rapid attack leaves minimal time for organisations to identify and take preventative action. This is worrying when considering the cost of BEC is predicted to more than tens of billions.
Research Reveals ‘Password’ is Still the Most Common Term used by Hackers to Breach Enterprise Networks
In a report of over 800 million breached passwords, vendor Specops identified some worrying results. Some of the key findings from the report include 88% of passwords used in successful attacks consisting of 12 characters or less and the most common base terms used in passwords involving ‘password’, ‘admin’, ‘welcome’ and ‘p@ssw0rd’. The report found that 83% of the compromised passwords satisfied both the length and complexity requirements of cyber security compliance standards such as NIST, GDPR, HIPAA and Cyber Essentials.
Just 10% of Firms Can Resolve Cloud Threats in an Hour
Two-thirds (39%) of global organisations reported a surge in breaches over the past year, with IT complexity increasing and detection and response capabilities worsening, according to Palo Alto Networks. It found that as enterprises move more of their data and workloads to the cloud, they’re finding it increasingly difficult to discover and remediate incidents quickly. Over two-fifths (42%) reported an increase in mean time to remediate, while 90% said they are unable to detect, contain and resolve cyber-threats within an hour. Nearly a third (30%) reported a major increase in intrusion attempts and unplanned downtime. Part of the challenge appears to be the complexity of their cloud security environments – partly caused by tool bloat.
https://www.infosecurity-magazine.com/news/10-firms-resolve-cloud-threats-hour/
MSPs in the Crosshairs of Ransomware Gangs
Many attacks have heightened attention around third-party risk and the security obligations of MSPs in meeting multiple customers’ IT needs. Attacks such as the ones on RackSpace and LastPass show that some ransomware actors are now intentionally targeting MSPs to access sensitive customer data. It is now believed that some advanced persistent threat (APT) groups could be stepping up their attacks on MSP’s in order to gain sensitive customer data.
https://www.msspalert.com/cybersecurity-research/msps-in-the-crosshairs-of-ransomware-gangs/
Stolen Credentials Increasingly Empower the Cyber Crime Underground
Threat Intelligence provider Flashpoint found that last year threat actors exposed or stole 22.62 billion credentials and personal records, which often make their way to underground forums and cyber criminal markets. This follows a significant increase in market activity; just last year Flashpoint recorded 190 new illicit markets emerge and the continual rise in attacks focused on stealing credentials only further empowers cyber crime underground.
It’s Time to Assess the Potential Dangers of an Increasingly Connected World
As global conflicts continue, cyber has become the fifth front of warfare. The world is approaching 50 billion connected devices, controlling everything from our traffic lights to our nuclear arsenal and we have already seen large-scale cyber attacks. Adding to this, a multitude of infrastructure runs on services ran by a handful of companies; Palo Alto Networks, Cisco and Fortinet control more than 50% of the market for security appliances. As such, an attack on one of these companies could cause a huge ripple effect on their customers.
Mounting Cyber Threats Mean Financial Firms Urgently Need Better Safeguards
According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF) 64% of banks and supervisory authorities do not mandate testing and exercising cyber security and 54% lack dedicated a cyber incident reporting regime. This increases the risk of experiencing a cyber attack. Regularly testing and exercising security will aid any organisation in its cyber resilience.
Insider Threat: Developers Leaked 10m Credentials Including Passwords in 2022
Security provider GitGuardian found that the rate at which developers leaked critical software secrets jumped by 0.5 to reach 5.5 out of every 1,000 commits to GitHub repositories; overall, this amounted to at least 10 million instances of secrets leaking to a public repository. Generic passwords accounted for the majority of leaked secrets (56%) and more than a third (38%) of leaks involved API keys, random number generator seeds and other sensitive strings. These leaks can have worrying consequences for organisations.
Cyber Threat Detections Surges 55% In 2022
Security Provider Trend Micro has said that it stopped 146 billion cyber threats in 2022, a 55% increase on the previous year and evidence of the increase of attacks ramping up. Trend Micro also found a 242% increase in the number of blocked malicious files and an 86% increase in backdoor malware detections with the latter showing an increase in attackers gaining initial access. Furthermore, the number of critical vulnerabilities in 2022 doubled compared to the previous year. Trend Micro noted that this is all likely due to an ever expanding attack surface of organisations.
https://www.infosecurity-magazine.com/news/cyberthreat-detections-surge-55/
European Central Bank Tells Banks to Run Cyber Stress Tests after Rise in Hacker Attacks
The European Central Bank (ECB) will ask all major lenders in the Eurozone to detail by next year, how they would respond to and recover from a successful cyber attack. The ECB is in the process of designing a scenario involving a theoretical breach of the financial system’s cyber defences, which will be sent to all of the 111 banks it assesses to see how they would react. The stress test stems from the increasing amount of cyber attacks. If cyber has shown us anything, it’s that anyone can be a target and performing a stress test would help any organisation prepare for the worst.
https://www.ft.com/content/f03d68a4-fdb9-4312-bda3-3157d369a4a6
Employees Are Feeding Sensitive Business Data to ChatGPT
1 in 20 employees have put sensitive corporate data into popular AI tool ChatGPT, raising concerns that this could result in massive leaks of proprietary information. In some cases, this has involved employees cutting and pasting strategic documents and asking ChatGPT to make a PowerPoint.
Is Ransomware Declining? Not So Fast Experts Say
Security provider CrowdStrike have explained that the perceived decline in ransomware reflects the abilities of threat actors to adapt, splinter and regroup against defensive measures. CrowdStrike expand on this, stating that whilst ransom payments dipped slightly in 2022, there was an uprise in data extortion and ransomware as a service (RaaS).
Preventing Corporate Data Breaches Starts with Remembering that Leaks have Real Victims
The impact a data breach can have on an individual is devastating and ultimately there’s not much an individual can do themselves if the organisation that holds their data isn’t taking the right steps. To best protect themselves and their clients’ data, organisations should look to have appropriate defence in depth controls, including effective asset management, an open security culture, close monitoring of access, utilising strong authentication and maintaining an awareness of the ever changing threat landscape.
https://www.helpnetsecurity.com/2023/03/07/preventing-corporate-data-breaches/
Faced With Likelihood of Ransomware Attacks, Businesses Still Choosing to Pay Up
In a recent report Proofpoint found that globally 76% of organisations experienced ransomware attempts, with 64% eventually infected. Amongst those that had a cyber insurance policy, 82% of insurers stepped up to pay the ransom either in full or partially. The report found that with the rise in number and sophistication of attacks it is more important than ever for proper security training and awareness in organisations.
Experts See Growing Need for Cyber Security Workers as One in Six Jobs go Unfilled
A report by the Information and Communications Technology Council (ICTC) found that 1 in 6 cyber security jobs are unfulfilled and this is only expected to grow in the coming years. The ICTC stated that “This is not just about education or government funding, but about companies willing to provide hands-on training and experience to the next generation of cyber security experts”.
Threats
Ransomware, Extortion and Destructive Attacks
Faced with likelihood of ransomware attacks, businesses still choosing to pay up | ZDNET
Is ransomware declining? Not so fast, experts say | TechTarget
FBI and CISA warn of increasing Royal ransomware attack risks (bleepingcomputer.com)
City of Oakland Faces Major Data Leak - Infosecurity Magazine (infosecurity-magazine.com)
Indigo Books Refuses LockBit Ransomware Demand (darkreading.com)
Core Members of DoppelPaymer Ransomware Gang Targeted in Germany and Ukraine (thehackernews.com)
Ransom House ransomware attack hit Hospital Clinic de Barcelona- - Security Affairs
Security Patch Management Strengthens Ransomware Defence (trendmicro.com)
Ransomware gang posts video of data stolen from Minneapolis schools (bleepingcomputer.com)
IceFire ransomware now encrypts both Linux and Windows systems (bleepingcomputer.com)
Examining Ransomware Payments From a Data-Science Lens (trendmicro.com)
Cyble — BlackSnake Ransomware Emerges from Chaos Ransomware's Shadow
Phishing & Email Based Attacks
AI is taking phishing attacks to a whole new level of sophistication - Help Net Security
Catches of the Month: Phishing Scams for March 2023 - IT Governance UK Blog
BEC – Business Email Compromise
Other Social Engineering; Smishing, Vishing, etc
Experts Warn of "SMS Pumping" Fraud Epidemic - Infosecurity Magazine (infosecurity-magazine.com)
Vishing attacks increasing, but AI's role still unclear | TechTarget
2FA/MFA
NCSC: Twitter Users Should Find MFA Alternatives - Infosecurity Magazine (infosecurity-magazine.com)
Malware
DrayTek VPN routers hacked with new malware to steal data, evade detection (bleepingcomputer.com)
Malicious PyPI package signals direction of cyber crime • The Register
How to prevent Microsoft OneNote files from infecting Windows with malware (bleepingcomputer.com)
Stealthy UEFI malware bypassing Secure Boot enabled by unpatchable Windows flaw | Ars Technica
New malware infects business routers for data theft, surveillance (bleepingcomputer.com)
Old Windows ‘Mock Folders’ UAC bypass used to drop malware (bleepingcomputer.com)
Emotet malware attacks return after three-month break (bleepingcomputer.com)
AI-Powered 'BlackMamba' Keylogging Attack Evades Modern EDR Security (darkreading.com)
New ScrubCrypt Crypter Used in Cryptojacking Attacks Targeting Oracle WebLogic (thehackernews.com)
Hackers Exploiting Remote Desktop Software Flaws to Deploy PlugX Malware (thehackernews.com)
Custom Chinese Malware Found on SonicWall Appliance - SecurityWeek
FBI and international cops catch a NetWire RAT • The Register
Mobile
Denial of Service/DoS/DDOS
Internet of Things – IoT
Data Breaches/Leaks
Credential Stuffing attack on Chick-fil-A impacted +71K users- Security Affairs
Popular fintech apps expose valuable, exploitable secrets - Help Net Security
PayPal Sued Over Data Breach that Impacted 35,000 users (hackread.com)
Acer Data Breach? Hacker Claims to Sell 160GB Trove of Stolen Data (hackread.com)
Data breach exposed millions of Verizon customers' account info (androidpolice.com)
Congress’ Social Security Numbers Leaked in DC Health Link Hack (gizmodo.com)
Data protection vendor Acronis admits to data leak • The Register
AT&T confirms 9m wireless accounts exposed by third part • The Register
Organised Crime & Criminal Actors
BidenCash leaks 2.1M stolen credit/debit cards- Security Affairs
Malicious PyPI package signals direction of cyber crime • The Register
Cryptocurrency/Cryptomining/Cryptojacking/NFTs/Blockchain
FTX Confirms $9 Billion in Customer Funds Vanished (gizmodo.com)
Russia-Ukraine war: How both sides of the conflict have used crypto to win (cointelegraph.com)
New ScrubCrypt Crypter Used in Cryptojacking Attacks Targeting Oracle WebLogic (thehackernews.com)
Insider Risk and Insider Threats
Fraud, Scams & Financial Crime
FTX Confirms $9 Billion in Customer Funds Vanished (gizmodo.com)
Experts Warn of "SMS Pumping" Fraud Epidemic - Infosecurity Magazine (infosecurity-magazine.com)
Scammers using voice-cloning A.I. to mimic relatives | Fortune
Alleged security breach leaves millions of dollars missing from Flutterwave accounts | TechCrunch
New Rise In ChatGPT Scams Reported By Fraudsters (informationsecuritybuzz.com)
Deepfakes
Insurance
Dark Web
Supply Chain and Third Parties
Snap CISO talks risky supply chain security business • The Register
SolarWinds IR lead: supply-chain attacks 'getting bigger' • The Register
AT&T confirms 9m wireless accounts exposed by third part • The Register
Software Supply Chain
Cloud/SaaS
Experts Reveal Google Cloud Platform's Blind Spot for Data Exfiltration Attacks (thehackernews.com)
Hackers are quickly learning how to target cloud systems (axios.com)
Attack Surface Management
Asset Management
Encryption
New TPM 2.0 flaws could let hackers steal cryptographic keys (bleepingcomputer.com)
New Steganography Breakthrough Enables “Perfectly Secure” Digital Communications (scitechdaily.com)
API
Open Source
Passwords, Credential Stuffing & Brute Force Attacks
Stolen credentials increasingly empower the cyber crime underground | CSO Online
Credential Stuffing attack on Chick-fil-A impacted +71K users- Security Affairs
The Role of Verifiable Credentials In Preventing Account Compromise (darkreading.com)
Young government workers show poor password management habits - Help Net Security
Social Media
NCSC: Twitter Users Should Find MFA Alternatives - Infosecurity Magazine (infosecurity-magazine.com)
Training, Education and Awareness
Regulations, Fines and Legislation
Governance, Risk and Compliance
Inadequate patches and advisories increase cyber risk - Help Net Security
Why do Businesses Need to Focus More on Cyber security (hackread.com)
Flashpoint: Threat vectors converging, increasing damage | TechTarget
How to achieve and shore up cyber resilience in a recession - Help Net Security
The cyber security landscape in the era of economic instability – Help Net Security
Models, Frameworks and Standards
Open letter demands OWASP overhaul, warns of mass project exodus | CSO Online
NIST Retooling Cyber security Framework to Reflect Changing Cyber scape – MSSP Alert
Data Protection
Careers, Working in Cyber and Information Security
Law Enforcement Action and Take Downs
Core Members of DoppelPaymer Ransomware Gang Targeted in Germany and Ukraine (thehackernews.com)
FBI and international cops catch a NetWire RAT • The Register
Privacy, Surveillance and Mass Monitoring
Secret Service and ICE break the law with fake phone towers • The Register
Thought you'd opted out of online tracking? Think again • The Register
Artificial Intelligence
AI is taking phishing attacks to a whole new level of sophistication - Help Net Security
Employees Are Feeding Sensitive Business Data to ChatGPT (darkreading.com)
You can poison AI datasets for just $60, a new study shows (fastcompany.com)
Thousands scammed by AI voices mimicking loved ones in emergencies | Ars Technica
Vishing attacks increasing, but AI's role still unclear | TechTarget
AI-Powered 'BlackMamba' Keylogging Attack Evades Modern EDR Security (darkreading.com)
Criminals will use ChatGPT to unleash wave of fraud, warns Darktrace (telegraph.co.uk)
Misinformation, Disinformation and Propaganda
Spyware, Cyber Espionage & Cyber Warfare, including Russian Invasion of Ukraine
What can security teams learn from a year of cyber warfare? | Computer Weekly
Pegasus spyware used to spy on a Polish mayor- Security Affairs
Russia-Ukraine war: How both sides of the conflict have used crypto to win (cointelegraph.com)
Sharp Panda targets government entities in Southeast Asia- Security Affairs
Managed Service Provider Identifies Potential Chinese Spy Ring - MSSP Alert
Chinese cyber spies target unpatched SonicWall gear • The Register
Nation State Actors
What can security teams learn from a year of cyber warfare? | Computer Weekly
Russia Bans Messengers, Including WhatsApp, Telegram, And More (informationsecuritybuzz.com)
Russia-Ukraine war: How both sides of the conflict have used crypto to win (cointelegraph.com)
China-aligned APT is exploring new technology stacks for malicious tools - Help Net Security
Sharp Panda targets government entities in Southeast Asia- Security Affairs
Managed Service Provider Identifies Potential Chinese Spy Ring - MSSP Alert
Chinese cyber spies target unpatched SonicWall gear • The Register
Lazarus group infiltrated South Korean finance firm twice last year | CSO Online
New Chinese regulatory body expected to streamline data governance rules | CSO Online
Vulnerability Management
Inadequate patches and advisories increase cyber risk - Help Net Security
Build Cyber Resiliency With These Security Threat-Mitigation Considerations
Zero Day Threat Protection for Your Network (trendmicro.com)
557 CVEs Added to CISA's Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog in 2022 - SecurityWeek
Machine Learning Improves Prediction of Exploited Vulnerabilities (darkreading.com)
Security Patch Management Strengthens Ransomware Defense (trendmicro.com)
VulnCheck: CISA's KEV missing 42 vulnerabilities from 2022 | TechTarget
Vulnerabilities
Researchers discover 'kill switch' in Starlink terminals - Security - iTnews
PoC exploit for recently patched Microsoft Word RCE is public (CVE-2023-21716) - Help Net Security
CISA's KEV Catalog Updated with 3 New Flaws Threatening IT Management Systems (thehackernews.com)
Exploitation of Critical Vulnerability in End-of-Life VMware Product Ongoing - SecurityWeek
Fortinet warns of new critical unauthenticated RCE vulnerability (bleepingcomputer.com)
Chinese cyber spies target unpatched SonicWall gear • The Register
Bitwarden flaw can let hackers steal passwords using iframes (bleepingcomputer.com)
Veeam warns to install patches to fix a bug in Backup & Replication- Security Affairs
Hackers Exploiting Remote Desktop Software Flaws to Deploy PlugX Malware (thehackernews.com)
Vulnerability Exposes Cisco Enterprise Routers to Disruptive Attacks - SecurityWeek
Jenkins Server Vulnerabilities Chained for Remote Code Execution - SecurityWeek
Other News
Biden Administration's Cyber security Strategy Takes Aim at Hackers (gizmodo.com)
Tracking device technology: A double-edged sword for CISOs | CSO Online
From Disinformation to Deep Fakes: How Threat Actors Manipulate Reality (thehackernews.com)
What CISOs need to understand about document signing - Help Net Security
Thousands of websites hacked as part of redirection campaign- Security Affairs
Sector Specific
Industry specific threat intelligence reports are available.
Contact us to receive tailored reports specific to the industry/sector and geographies you operate in.
· Automotive
· Construction
· Critical National Infrastructure (CNI)
· Defence & Space
· Education & Academia
· Energy & Utilities
· Estate Agencies
· Financial Services
· FinTech
· Food & Agriculture
· Gaming & Gambling
· Government & Public Sector (including Law Enforcement)
· Health/Medical/Pharma
· Hotels & Hospitality
· Insurance
· Legal
· Manufacturing
· Maritime
· Oil, Gas & Mining
· OT, ICS, IIoT, SCADA & Cyber-Physical Systems
· Retail & eCommerce
· Small and Medium Sized Businesses (SMBs)
· Startups
· Telecoms
· Third Sector & Charities
· Transport & Aviation
· Web3
As usual, contact us to help assess where your risks lie and to ensure you are doing all you can do to keep you and your business secure.
Look out for our ‘Cyber Tip Tuesday’ video blog and on our YouTube channel.
You can also follow us on Facebook, Twitter and LinkedIn.
Links to articles are for interest and awareness and linking to or reposting external content does not endorse any service or product, likewise we are not responsible for the security of external links.
Black Arrow Cyber Threat Briefing 18 December 2020
Black Arrow Cyber Threat Briefing 18 December 2020: The great hack attack - SolarWinds breach exposes big gaps in cyber security; A wake-up for the world on cyber security; White House activates cyber emergency response; US nuclear weapons agency targeted; UK companies targeted; Increasing Risk of Cyber Attacks; millions of users install malicious browser extensions; C19 Vaccines sold on dark web
Welcome to this week’s Black Arrow Cyber Threat Briefing – a weekly digest, collated and curated by our cyber experts to provide senior and middle management with an easy to digest round up of the most notable threats, vulnerabilities and cyber related news from the last week.
Top Cyber Headlines of the Week
The great hack attack: SolarWinds breach exposes big gaps in cyber security
Until this week, SolarWinds was a little known IT software group from Texas. Its deserted lobby has a framed magazine article from a few years ago when it was on a list of America’s “Best Small Companies”.
Now the Austin-based company is at the heart of one of the biggest and most startling cyber hacks in recent history, with ramifications that extend into the fields of geopolitics, espionage and national security.
For nine months, sophisticated state-backed hackers have exploited a ubiquitous SolarWinds software product in order to spy on government and business networks around the world, including in the US, UK, Israel and Canada. Wielding innovative tools and tradecraft, the cyber spies lurked in email services, and posed as legitimate staffers to tap confidential information stored in the cloud.
The bombshell revelations have sent 18,000 exposed SolarWinds customers scrambling to assess whether outsiders did indeed enter their systems, what the damage was and how to fix it.
https://www.ft.com/content/c13dbb51-907b-4db7-8347-30921ef931c2
A wake-up for the world on cyber security
Imagine intruders break into your home and loiter undetected for months, spying on you and deciding which contents to steal. This in essence is the kind of access that hackers, assumed to be Russian, achieved in recent months at US government institutions including the Treasury and departments of commerce and homeland security, and potentially many US companies. If the fear in the Cold War was of occasional “moles” gaining access to secrets, this is akin to a small army of moles burrowing through computer systems. The impact is still being assessed, but it marks one of the biggest security breaches of the digital era.
https://www.ft.com/content/d3fc0b14-4a82-4671-b023-078516ea714e
US government, thousands of businesses now thought to have been affected by SolarWinds security attack
Thousands of businesses and several branches of the US government are now thought to have been affected by the attack on software firm SolarWinds.
The Austin-based company has fallen victim to a massive supply chain attack believed to be the work of state-sponsored hackers.
Along with the US treasury and commerce departments, the Department of Homeland Security is now thought to have been affected by the attack. In a statement to the SEC today, SolarWinds said it had notified 33,000 customers of its recent hack, but that only 18,000 of these used the affected version of its Orion platform.
https://www.techradar.com/uk/news/solarwinds-suffers-massive-supply-chain-attack
White House activates cyber emergency response under Obama-era directive
In the wake of the SolarWinds breach, the National Security Council has activated an emergency cyber security process that is intended to help the government plan its response and recovery efforts, according to White House officials and other sources.
The move is a sign of just how seriously the Trump administration is taking the foreign espionage operation, former NSC officials told CyberScoop.
The action is rooted in a presidential directive issued during the Obama administration known as PPD-41, which establishes a Cyber Unified Coordination Group (UCG) that is intended to help the U.S. government coordinate multiple agencies’ responses to the significant hacking incident.
The UCG is generally led by the Department of Justice — through the FBI and the National Cyber Investigative Joint Task Force — as well as the Office of the Director of National Intelligence and the Department of Homeland Security.
https://www.cyberscoop.com/solarwinds-white-house-national-security-council-emergency-meetings/
Hackers targeted US nuclear weapons agency in massive cyber security breach, reports say
The National Nuclear Security Administration and Energy Department, which safeguard the US stockpile of nuclear weapons, have had their networks hacked as part of the widespread cyber espionage attack on a number of federal agencies.
Politico reports that officials have begun coordinating notifications about the security breach to the relevant congressional oversight bodies.
Suspicious activity was identified in the networks of the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC), Los Alamos and Sandia national laboratories in New Mexico and Washington, the Office of Secure Transportation, and the Richland Field Office of the Department of Energy.
Officials with direct knowledge of the matter said hackers have been able to do more damage to the network at FERC, according to the report.
Microsoft warns UK companies were targeted by SolarWinds hackers
Microsoft has warned that some of its UK customers have been exposed to the malware used in the Russia-linked SolarWinds hack that targeted US states and government agencies.
More than 40 of the tech giant's customers are thought to have used breached SolarWinds software, including clients in Britain, the US, Canada, Mexico, Belgium, Spain, Israel, and the UAE.
The company would not name the victims, but said they include government agencies, think tanks, non-governmental organisations and IT firms. Microsoft said four in five were in the US, with nearly half of them tech companies.
“This is not ‘espionage as usual,’ even in the digital age,” said Brad Smith, Microsoft's president. “Instead, it represents an act of recklessness that created a serious technological vulnerability for the United States and the world.”
The attackers, believed to be working for the Russian government, got into computer networks by installing a vulnerability in Orion software from SolarWinds.
Society at Increasingly High Risk of Cyber Attacks
Cyber attacks are becoming easier to conduct while conversely security is getting increasingly difficult, according to Kevin Curran, senior IEEE member and professor of cyber security, Ulster University, during a virtual media roundtable.
“Any company you can think of has had a data breach,” he commented. “Whenever a data breach happens it weakens our credentials because our passwords are often reused on different websites.”
He observed that the art of hacking doesn’t necessarily require a significant amount of technical expertise anymore, and bad actors can receive substantial help from numerous and readily accessible tools online. “You don’t have to spend seven years in college to learn how to hack, you just have to know about these sites and what terms to use,” noted Curran.
A number of legitimate online mechanisms that can help damaging attacks to be launched by hackers were highlighted by Curran in his presentation. These include Google Dorks, which are “search strings which point to website vulnerabilities.” This means vulnerable accounts can be identified simply via Google searches.
https://www.infosecurity-magazine.com/news/society-increasingly-risk-cyber/
Three million users installed 28 malicious Chrome or Edge extensions
More than three million internet users are believed to have installed 15 Chrome, and 13 Edge extensions that contain malicious code, security firm Avast said today.
The 28 extensions contained code that could perform several malicious operations, including:
-redirect user traffic to ads
-redirect user traffic to phishing sites
-collect personal data, such as birth dates, email addresses, and active devices
-collect browsing history
-download further malware onto a user's device
But despite the presence of code to power all the above malicious features, Avast researchers said they believe the primary objective of this campaign was to hijack user traffic for monetary gains.
https://www.zdnet.com/article/three-million-users-installed-28-malicious-chrome-or-edge-extensions/
Vaccines for sale on dark web as criminals target pandemic profits
Black market vendors were offering coronavirus vaccines for sale on hidden parts of the internet days after the first Covid-19 shot was approved this month, as criminals seek to profit from global demand for inoculations.
One such offer on the so-called dark web, traced by cyber security company Check Point Software, was priced at $250 with the seller promising “stealth” delivery in double-wrapped packaging. Shipping from the US via post or a leading courier company would cost $20, with an extra $5 securing overnight delivery.
https://www.ft.com/content/8bfc674e-efe6-4ee0-b860-7fcb5716bed6
Threats
Ransomware
FBI says DoppelPaymer ransomware gang is harassing victims who refuse to pay
House purchases in Hackney fall through following cyber attack against council
Mount Locker Ransomware Offering Double Extortion Scheme to Other Hackers
Ransomware operators use SystemBC RAT as off-the-shelf Tor backdoor
Phishing
Subway Sandwich Loyalty-Card Users Suffer Ham-Handed Phishing Scam
Microsoft Office 365 Credentials Under Attack By Fax ‘Alert’ Emails
IoT
Malware
New iOS and Android spyware responsible for multi-layered sextortion campaign
Google Chrome, Firefox, Edge hijacked by massive malware attack: What you need to know
This nasty malware is infecting every web browser — what to do now
Tor malware is becoming a worryingly popular ransomware tool
Vulnerabilities
Israeli Phone-hacking Firm Claims It Can Now Break Into Encrypted Signal App
PgMiner botnet exploits disputed CVE to hack unsecured PostgreSQL DBs
Zero-day in WordPress SMTP plugin abused to reset admin account passwords
Sophos fixes SQL injection vulnerability in their Cyberoam OS
Wormable code-execution flaw in Cisco Jabber has a severity rating of 9.9 out of 10
Data Breaches
Twitter hit with €450,000 GDPR fine nearly two years after disclosing data breach
Data Leak Exposes Details of Two Million Chinese Communist Party Members
Organised Crime
Nation State Actors
Privacy
UK police unlawfully processing over a million people’s data on Microsoft 365
Sci-fi surveillance: Europe's secretive push into biometric technology
Other News
Reports Published in the Last Week
As usual, contact us to help assess where your risks lie and to ensure you are doing all you can do to keep you and your business secure.
Look out for our weekly ‘Cyber Tip Tuesday’ video blog and on our YouTube channel.
You can also follow us on Facebook, Twitter and LinkedIn.
Links to articles are for interest and awareness and linking to or reposting external content does not endorse any service or product, likewise we are not responsible for the security of external links.
Cyber Weekly Flash Briefing 25 September 2020: GFSC consult on new Cyber Rules; FinCEN leak exposes poor data security; Zerologon attacks detected; ransomware gang behind German hospital death
Cyber Weekly Flash Briefing 25 September 2020: GFSC consulting on new Cyber Rules; Leaked FinCEN files expose poor data security; Microsoft detects active Zerologon attacks; ransomware crew fingered for German hospital death; malware that steals your most sensitive data on the rise; Ransomware is evolving; top threats inside malicious emails; Credential Stuffing behind Recent Attacks
Links to articles are for interest and awareness and linking to or reposting external content does not endorse any service or product, likewise we are not responsible for the security of external links.
GFSC new Cyber Rules and Guidance out for consultation
The GFSC have put the Cyber Security Rules and Guidance Consultation Paper up on their website and consultation hub.
Why this matters:
The new rules and accompanying guidance came out of the 18 month thematic review which ended last year, which found that regulated financial service firms within the Bailiwick of Guernsey were not taking risks from cyber threats seriously enough and were lacking in appropriate protections and controls. These new rules seek to rectify this but many firms on the Island are going to have to do work to become compliant, especially around their ability to monitor for and detect unusual activity that could be indicative of a actual or attempted intrusion or breach.
The rules and guidance can be found here:
Leaked FinCEN files expose poor data security
Leaked documents, dubbed the “FinCEN Files,” describe global money laundering of $2 trillion processed by many of the world’s biggest banks between 2000 and 2017. The reveal illuminates the struggle for the financial industry and government to provide ironclad data protection.
“This sensational and unprecedented leak clearly demonstrates a wide spectrum of data protection weaknesses in the governmental sector, affecting even the most developed Western countries,” Ilia Kolochenko, founder and CEO of ImmuniWeb, said of the files.
“From a cybersecurity standpoint, we may expect a growing lack of trust to governmental agencies, which on one side have quasi-unlimited access to the most sensitive data of the largest organisations, while cannot duly safeguard this data on the other side,” he said.
The latest disclosure exposing apparently insufficient attempts by the public and private sectors to curb corruption came to light in a BuzzFeed News report which detailed more than 2,500 reported cases, including 2,100 Suspicious Activity Reports (SAR) filed by financial institutions with the U.S. Treasury Department’s Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN).
JPMorgan Chase, Citigroup, Bank of America, Deutsche Bank, HSBC and Standard Chartered are among the financial institutions cited in the leaked files as processing dirty money around the world. The documents may have come from a whistleblower or insider at FinCEN. The International Consortium of Investigative Journalists (ICIJ), which represents 108 news organizations in 88 countries, is conducting a probe of the matter.
Why this matters:
Other similar investigative reports on similar wrongdoing focused single financial, tax or legal institutions, such as the 2017 Panama Papers emanating from clients of the law firm Mossack Fonseca. But the FinCEN docs reveal that a wide array of people from oligarchs and corrupt politicians to drug dealers and organised crime throughout the world know how to circumvent the system’s supposed checks and balances.
Read more: https://www.scmagazine.com/home/security-news/leaked-fincen-files-expose-poor-data-security/
Microsoft says it detected active attacks leveraging Zerologon vulnerability
Hackers are actively exploiting the Zerologon vulnerability in real-world attacks, Microsoft's security intelligence team said this week.
The attacks were expected to happen, according to security industry experts.
Multiple versions of weaponized proof-of-concept exploit code have been published online in freely downloadable form since details about the Zerologon vulnerability were revealed a week ago.
The first proof-of-concept exploit was published hours after the explanatory blog post, confirming initial analysis that the Zerologon bug is easy to exploit, even by low-skilled threat actors.
Why this matters:
Put simply the Zerologon bug is a vulnerability in Netlogon, the protocol used by Windows systems to authenticate against a Windows Server running as a domain controller. Exploiting the Zerologon bug can allow hackers to take over the domain controller, and inherently a company's internal network.
Zerologon was described by many as the most dangerous bug revealed this year. US federal agencies were given three days to patch domain controllers or disconnect them from federal networks.
As several security experts have recommended since Microsoft revealed the attacks, companies that have their domain controller exposed on the internet should take systems offline to patch them.
These internet-reachable servers are particularly vulnerable as attacks can be mounted directly, without the hacker first needing a foothold on internal systems.
Doppelpaymer ransomware crew fingered for attack on German hospital that caused death of a patient
The Doppelpaymer ransomware gang were behind the cyber-attack on a German hospital that led to one patient's death, according to local sources.
A German newspaper carried a report that Doppelpaymer's eponymous ransomware had been introduced to the University Hospital Düsseldorf's network through a vulnerable Citrix product.
That ransomware infection, activated last week, is said by local prosecutors to have led to the death of one patient who the hospital was unable to treat on arrival. She died in an ambulance while being transported to another medical facility with functioning systems.
Why this matters:
According to a report handed to the provincial government of North Rhine-Westphalia and seen by the German Press Association (DPA), the ransomware's loader had been lurking on the hospital's network since December 2019, the same month a patch was issued by Citrix for CVE-2019-19781 – the same vuln exploited to hit the hospital.
Whilst this is the first time a loss of life has been directly attributed to ransomware the threats are increasing all the time.
Vulnerabilities must be patched as soon as possible to stop known vulnerabilities from being used in attacks.
Read more: https://www.theregister.com/2020/09/23/doppelpaymer_german_hospital_ransomware/
“LokiBot,” the malware that steals your most sensitive data, is on the rise
Agencies in the US have reported seeing a big uptick in infections coming from LokiBot, an open source DIY malware package for Windows that’s openly sold or traded for free in underground forums. It steals passwords and cryptocurrency wallets, and it can also download and install new malware.
The increase was measured by an automated intrusion-detection system for collecting, correlating, analysing, and sharing computer security information.
US cyber agency CISA observed a notable increase in the use of LokiBot malware by malicious cyber actors since July 2020 according to an alert issued this week.
Why this matters:
While not quite as prevalent or noxious as the Emotet malware, LokiBot remains a serious and widespread menace. The infostealer spreads through a variety of methods, including malicious email attachments, exploitation of software vulnerabilities, and trojans sneaked into pirated or free apps. Its simple interface and reliable codebase make it attractive to a wide range of crooks, including those who are new to cybercrime and have few technical skills.
Ransomware is evolving, but the key to preventing attacks remains the same
Ransomware attacks are getting more aggressive according to a senior figure at Europe's law enforcement agency, but there are simple steps which organisations can follow to protect themselves – and their employees – from falling victim to attacks.
"Ransomware is one of the main threats," said the head of operations at Europol's European Cybercrime Centre (EC3). Europol supports the 27 EU member states in their fight against terrorism, cybercrime and other serious and organised forms of crime.
"Criminals behind ransomware attacks are adapting their attack vectors, they're more aggressive than in the past – they're not only encrypting the files, they're also exfiltrating data and making it available," he explained. "From a law enforcement perspective, we have been monitoring this evolution."
Why this matters:
This year has seen a rise in ransomware attacks where cyber criminals aren't just encrypting the networks of victims and demanding six-figure bitcoin payment to return the files, but they're also threatening to publish sensitive corporate information and other stolen data if the victim doesn't pay the ransom.
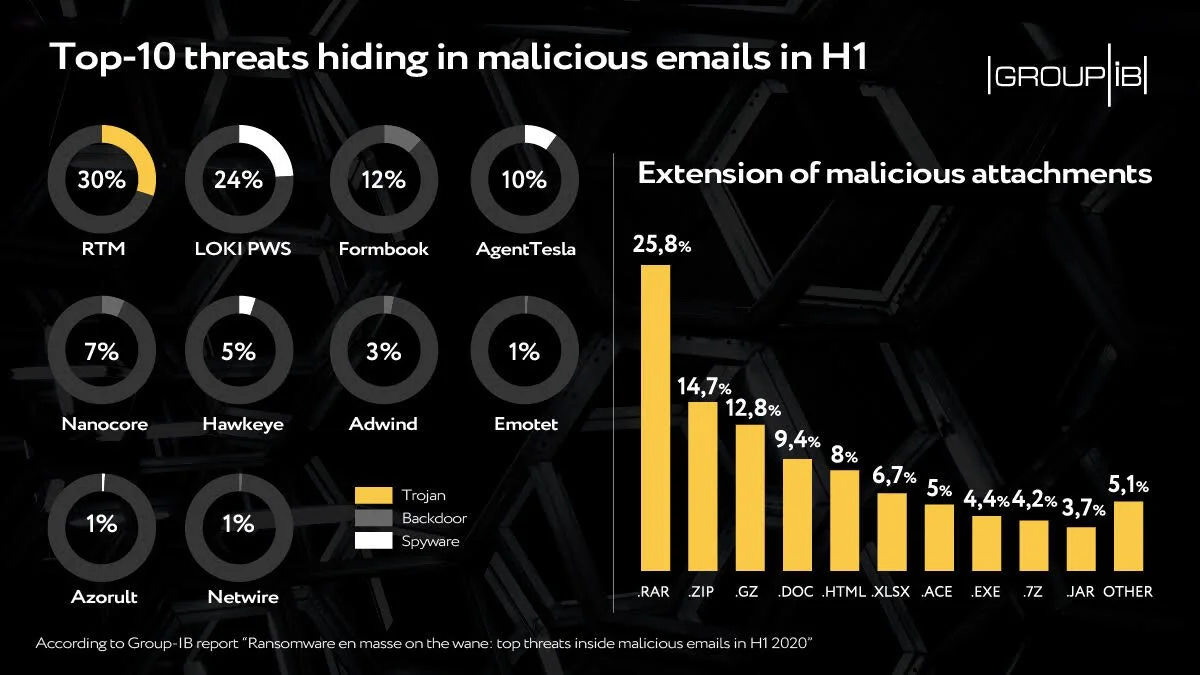
A look at the top threats inside malicious emails
Web-phishing targeting various online services almost doubled during the COVID-19 pandemic: it accounted for 46 percent of the total number of fake web pages, Group-IB reveals.
Ransomware, the headliner of the previous half-year, walked off stage: only 1 percent of emails analysed contained this kind of malware. Every third email, meanwhile, contained spyware, which is used by threat actors to steal payment data or other sensitive info to then put it on sale in the darknet or blackmail its owner.
Downloaders, intended for the installation of additional malware, and backdoors, granting cybercriminals remote access to victims’ computers, also made it to top-3. They are followed by banking Trojans, whose share in the total amount of malicious attachments showed growth for the first time in a while.
According to the data, in H1 2020 detected malicious emails were:
43 percent of the malicious mails had attachments with spyware or links leading to their downloading
17 percent contained downloaders
16 percent had backdoors
15 percent had banking trojans
Ransomware, which in the second half of 2019 hid in every second malicious email, almost disappeared from the mailboxes in the first six months of this year with a share of less than 1 percent.
Why this matters:
These findings confirm adversaries’ growing interest in Big Game Hunting. Ransomware operators have switched from attacks en masse on individuals to corporate networks. Thus, when attacking large companies, instead of infecting the computer of a separate individual immediately after the compromise, attackers use the infected machine to move laterally in the network, escalate the privileges in the system and distribute ransomware on as many hosts as possible.
Read more: https://www.helpnetsecurity.com/2020/09/21/top-threats-inside-malicious-emails/
Credential Stuffing: the Culprit of Recent Attacks
A year ago, researchers found that 2.2 billion leaked records, known as Collection 1-5, were being passed around by hackers. This ‘mega leak’ included 1.2 billion unique email addresses and password combinations, 773 million unique email addresses and 21 million plaintext passwords. With this treasure trove, hackers can simply test email and password combinations on different sites, hoping that a user has reused one. This popular technique is known as credential stuffing and is the culprit of many recent data breaches.
There are only a few months left of 2020 but this year has seen its fair share of major data breaches including:
Marriott International experienced another mega breach, when it was still recovering from the 2018 data breach that exposed approximately 339 million customer records
Zoom became a new favourite for hackers due to the remote working mandated in many parts of the world - in early April Zoom fell victim to a credential stuffing attack, which resulted in 500,000 of Zoom’s usernames and passwords being exposed on the Dark Web.
GoDaddy, the world’s largest domain registrar confirmed in April that credentials of 28,000 of its customer web hosting accounts were compromised in a security incident back in October 2019.
Nintendo - in March, users reported unauthorised logins to their accounts and charges for digital items without their permission. In June Nintendo advised that approximately 300,000 accounts were affected by the breach, resulting in the compromise of personal identifiable information such as email address, date of birth, country and gender.
Why this matters:
It has become evident that many of the recent data breaches were the result of credential stuffing attacks leveraging compromised passwords or passphrases. Credential stuffing attacks are automated hacks where stolen usernames and password combinations are thrown at the login process of various websites in an effort to break in. With billions of compromised credentials already circulating the Dark Web, credential stuffing attacks can be carried out with relative ease and with a 1-3% success rate.
When the account of an employee is compromised, hackers can gain access to sensitive data that organisation has collected, and sell it on the Dark Web. The stolen data, often including login credentials, can then be used to infiltrate other organisations’ systems which creates a never-ending cycle.
This is why the LinkedIn breach was blamed for several secondary compromises due to users recycling their exposed LinkedIn passwords on other sites.
Read more: https://www.infosecurity-magazine.com/blogs/credential-stuffing-recent-attacks/