Threat Intelligence Blog

Contact us to discuss any insights from our Blog, and how we can support you in a tailored threat intelligence report.
Black Arrow Cyber Threat Briefing 20 August 2021
Black Arrow Cyber Threat Briefing 20 August 2021:
-Third of Global Companies Have Experienced Ransomware Attack, Survey Finds
-Company Size Is A Nonissue With Automated Cyberattack Tools
-60% Of Employees Reuse Passwords Across Business And Personal Accounts
-LockBit 2.0 Ransomware Proliferates Globally
-Secret Terrorist Watchlist With 2 Million Records Exposed Online
-Phishing Costs Quadruple Over 6 Years
-Security Teams Report Rise In Cyber Risk
-Phishing Attacks Increase In H1 2021, Sharp Jump In Crypto Attacks
Welcome to this week’s Black Arrow Cyber Threat Briefing – a weekly digest, collated and curated by our cyber experts to provide senior and middle management with an easy to digest round up of the most notable threats, vulnerabilities, and cyber related news from the last week.
Top Cyber Stories of the Last Week
A Third of Global Companies Have Experienced Ransomware Attack, Survey Finds
Roughly a third of large international companies have faced a ransomware attack or other data breach in the last 12 months, according to a new survey.
Analysts surveyed almost 800 companies and found 37% of international companies experienced ransomware attacks this past year. The survey focused on companies with more than 500 employees.
Company Size Is A Nonissue With Automated Cyber Attack Tools
Even with plenty of old problems to contend with, firms need to get ready for new and more powerful automated ransomware tools.
Cyber criminals are constantly looking for the best return on their investment and solutions that lower the chance of being caught. Sadly, that appears to mean small businesses are their current target of opportunity.
Tech media and cyber pundits have been sounding the alarm and offering small businesses specific cybersecurity solutions for a few years now, but it seems to no avail.
https://www.techrepublic.com/article/company-size-is-a-nonissue-with-automated-cyberattack-tools/
Over 60% Of Employees Reuse Passwords Across Business And Personal Accounts
Nearly two thirds of employees are using personal passwords to protect corporate data, and vice versa, with even more business leaders concerned about this very issue. Surprisingly, 97% of employees know what constitutes a strong password, yet over half (53%) admit to not always using one.
http://hrnews.co.uk/over-60-of-employees-reuse-passwords-across-business-and-personal/
LockBit 2.0 Ransomware Proliferates Globally
Fresh attacks target companies’ employees, promising millions of dollars in exchange for valid account credentials for initial access.
The LockBit ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) gang has ramped up its targeted attacks, researchers said, with attempts against organizations in Chile, Italy, Taiwan and the U.K. using version 2.0 of its malware.
https://threatpost.com/lockbit-ransomware-proliferates-globally/168746/
Secret Terrorist Watchlist With 2 Million Records Exposed Online
A secret terrorist watchlist with 1.9 million records, including classified "no-fly" records was exposed on the internet.
The list was left accessible on an Elasticsearch cluster that had no password on it.
Phishing Costs Nearly Quadrupled Over 6 Years
Lost productivity & mopping up after the costly attacks that follow phishing – BEC & ransomware in particular – eat up most costs, not pay-outs to crooks.
Research shows that the cost of phishing attacks has nearly quadrupled over the past six years: Large US companies are now losing, on average, $14.8 million annually, or $1,500 per employee.
That’s up sharply from 2015’s figure of $3.8 million, according to a new study from Ponemon Institute that was sponsored by Proofpoint.
According to the study, released Tuesday, phishing leads to some of the costliest cyber attacks.
https://threatpost.com/phishing-costs-quadrupled/168716/
Security Teams Report Rise In Cyber Risk
A recent report shows declining confidence in many organisations’ security function to address today’s threats.
80% of respondents to the Trend Micro’s biannual Cyber Risk Index (CRI) report said they expect to experience a data breach that compromises customer data in the next 12 months.
The report surveyed more than 3,600 businesses of all sizes and industries across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and Latin America for their thoughts on cyber risk. Despite an increased focus on security due to high-profile ransomware and other attacks in the past year, respondents reported a rise in risk due to inadequate security processes like backing up key assets.
Organisations are overwhelmed as they pivot from traditional to distributed networks. Pandemic-driven work-from-home growth is potentially how businesses will be run going forward. That distributed network means that it’s harder for IT staff to know what assets are under their control and what security controls should be in place. With the line blurring between corporate and personal assets, organizations are overwhelmed with the pace of change.
https://www.csoonline.com/article/3629477/security-teams-report-rise-in-cyber-risk.html
Organisations Aware Of The Importance Of Zero Trust, Yet Still Relying On Passwords
Organisations have become more security conscious over the course of the pandemic, leading them to invest heavily in zero trust, according to a new study.
The report surveyed over 600 global security leaders about their initiatives and found that remote work has led to a change in how organizations view the importance of zero trust, with financial services, healthcare organisations and the software industry seeing the most significant progress.
78% of companies globally say that zero trust has increased in priority and nearly 90% are currently working on a zero trust initiative, up from just 41% a year ago.
https://www.helpnetsecurity.com/2021/08/11/importance-of-zero-trust/
Reliance On Third Party Workers Making Companies More Vulnerable To Cyber Attacks
A new survey revealed 83% of respondents agree that because organisations increasingly rely on contractors, freelancers, and other third party workers, their data systems have become more vulnerable to cyber attacks.
Further, 88% of people say organisations and government entities must have better data security systems in place to protect them from the increase in third party remote attacks.
Recent high-profile breaches, including SolarWinds, Colonial Pipeline, and JBS Foods, have exposed how vulnerable organisations are to cyber crime and in particular ransomware attacks. Of note with recent attacks is how data breaches can quickly affect aspects of everyday life, such as the ability to fill a car with petrol or buy meat at the supermarket.
https://www.helpnetsecurity.com/2021/08/16/reliance-on-third-party-workers/
The Cyber Security Skills Gap Persists For The Fifth Year Running
Most organisations are still lacking talent, according to a new report, but experts think expanding the definition of a cybersecurity professional can help.
T-Mobile Hack Is A Return To The Roots Of Cyber Crime
In the world of cyber crime, ransomware attacks might be the sophisticated bank heists. The hack of T-Mobile is more akin to smashing a window, grabbing merchandise, and running.
The attack that exposed the personal information of millions of T-Mobile customers spotlights a common type of cyber threat that can inflict significant damage to consumers, much like the recent rash of ransomware attacks hitting companies.
The breach exposed the data of more than 40 million people, T-Mobile confirmed Wednesday, including customer’s full names and driver’s license information. A hacker posted about the stolen information on a cyber crime forum late last week, offering to sell the information to buyers for the price of six bitcoin, or about $270,000.
This type of attack, in which hackers worm their way into companies’ systems, steal data and try to sell it online, has been a common tactic for years, cyber security experts say. Unlike the high-profile ransomware attacks that have disrupted fuel supplies, hospital systems and food production in recent months, these data exfiltration hacks do not lock down computer systems.
https://www.washingtonpost.com/technology/2021/08/19/tmobile-breach-data-hacks/
Phishing Attacks Increase In H1 2021, Sharp Jump In Crypto Attacks
The first half of 2021 shows a 22 percent increase in the volume of phishing attacks over the same time period last year, a new report reveals. Notably, however, phishing volume in June dipped dramatically for the first time in six months, immediately following a very high-volume in May.
Bad actors continue to utilise phishing to fleece proprietary information, and are developing more sophisticated ways to do so based on growth in areas such as cryptocurrency and sites that use single-sign-on.
https://www.helpnetsecurity.com/2021/08/19/phishing-attacks-h1-2021/
Connected Devices Increasingly At Risk As New Ransomware Attacks Are Reported Almost Daily
A new report has shined a light on the state of connected devices. The number of agentless and un-agentable devices increased to 42% in this year’s report (compared to 32% of agentless or un-agentable devices in 2020). These devices include medical and manufacturing devices that are critical to business operations along with network devices, IP phones, video surveillance cameras and facility devices (such as badge readers) that are not designed with security in mind, cannot be patched, and cannot support endpoint security agents.
With almost half of devices in the network that are either agentless or un-agentable, organisations need to complement their endpoint security strategy with a network-based security approach to discover and secure these devices.
https://www.helpnetsecurity.com/2021/08/12/connected-devices-risks/
Threats
Ransomware
John Oliver On Ransomware Attacks: ‘It’s In Everyone’s Interest To Tet This Under Control’
Device Complexity Leaving Schools At Heightened Risk Of Ransomware Attacks
This Ransomware Has Returned With New Techniques To Make Attacks More Effective
Diavol Ransomware Sample Shows Stronger Connection To TrickBot Gang
Ransomware Criminals' Demands Rise As Aggressive Tactics Pay Off
BEC
Phishing
Other Social Engineering
Malware
Malware Campaign Uses Clever 'Captcha' To Bypass Browser Warning
Malware Dev Infects Own PC And Data Ends Up On Intel Platform
Researchers Discover New AdLoad Malware Campaigns Targeting Macs And Apple Products
Mobile
IOT
Vulnerabilities
Multiple Flaws Affecting Realtek Wi-Fi SDKs Impact Nearly A Million IoT Devices
Unpatched Remote Hacking Flaw Disclosed In Fortinet's FortiWeb WAF
65 Vendors Affected By Severe Vulnerabilities In Realtek Chips
Eight-Year-Old Bug In Microsoft's 64-Bit VBA Prompts Complaints Of Neglect
Cisco Won’t Fix Zero-Day RCE Vulnerability In End-Of-Life VPN Routers
Data Breaches/Leaks
Chase Bank Accidentally Leaked Customer Info To Other Customers
Colonial Pipeline Reports Data Breach After May Ransomware Attack
Ford Bug Exposed Customer And Employee Records From Internal Systems
Dark Web
Dark Web Blockchain Analysis Tool Suspended After Flurry Of Media Coverage
Dark Web Drug Dealer Indicted For Laundering $137 Million In Bitcoin From Prison
Dark Web Criminals Have Built A Tool That Checks For Dirty Bitcoin
Supply Chain
DoS/DDoS
OT, ICS, IIoT and SCADA
Nation State Actors
Cloud
Other News
Threat Actors Hacked US Census Bureau In 2020 By Exploiting A Citrix Flaw
Cyber Security Is Top Priority For Enterprises As They Shift To Digital-First Operating Models
SMEs Awareness Of GDPR Is High, But Few Adhere To Its Legal Requirements
Hacker Finds A Way To Steal Windows 365 User Names And Passwords
As usual, contact us to help assess where your risks lie and to ensure you are doing all you can do to keep you and your business secure.
Look out for our weekly ‘Cyber Tip Tuesday’ video blog and on our YouTube channel.
You can also follow us on Facebook, Twitter and LinkedIn.
Links to articles are for interest and awareness and linking to or reposting external content does not endorse any service or product, likewise we are not responsible for the security of external links.
Black Arrow Cyber Threat Briefing 06 August 2021
Black Arrow Cyber Threat Briefing 06 August 2021:
-Ransomware Volumes Hit Record High
-Ransomware Gangs Recruiting Insiders To Breach Corporate Networks
-More Than 12,500 Vulnerabilities Disclosed In First Half Of 2021
-New DNS Vulnerability Allows 'Nation-State Level Spying' On Companies
-Constant Review Of Third Party Security Critical As Ransomware Threat Climbs
-Kaseya Ransomware Attack Sets Off Race To Hack Service Providers
-Joint UK/US Advisory Detailing Top 30 Vulnerabilities Include Plenty Of Usual Suspects
Welcome to this week’s Black Arrow Cyber Threat Briefing – a weekly digest, collated and curated by our cyber experts to provide senior and middle management with an easy to digest round up of the most notable threats, vulnerabilities, and cyber related news from the last week.
Top Cyber Stories of the Last Week
Ransomware Volumes Hit Record Highs As 2021 Wears On
Ransomware has seen a significant uptick so far in 2021, with global attack volume increasing by 151 percent for the first six months of the year as compared with the year-ago half. Meanwhile, the FBI has warned that there are now 100 different strains circulating around the world. From a hard-number perspective, the ransomware scourge hit a staggering 304.7 million attempted attacks. To put that in perspective, the firm logged 304.6 million ransomware attempts for the entirety of 2020.
https://threatpost.com/ransomware-volumes-record-highs-2021/168327/
Ransomware Gangs Recruiting Insiders To Breach Corporate Networks
The LockBit 2.0 ransomware gang is actively recruiting corporate insiders to help them breach and encrypt networks. In return, the insider is promised million-dollar payouts. Many ransomware gangs operate as a Ransomware-as-a-Service, which consists of a core group of developers, who maintain the ransomware and payment sites, and recruited affiliates who breach victims' networks and encrypt devices. Any ransom payments that victims make are then split between the core group and the affiliate, with the affiliate usually receiving 70-80% of the total amount. However, in many cases, the affiliates purchase access to networks from other third-party pentesters rather than breaching the company themselves. With LockBit 2.0, the ransomware gang is trying to remove the middleman and instead recruit insiders to provide them access to a corporate network.
More Than 12,500 Vulnerabilities Disclosed In First Half Of 2021
Two new reports were released, covering data breaches and vulnerabilities in the first half of 2021, finding that there was a decline in the overall number of reported breaches but an increase in the number of vulnerabilities disclosed. The company's data breach report found that there were 1,767 publicly reported breaches in the first six months of 2021, a 24% decline compared to the same period last year. The number of reported breaches grew in the US by 1.5% while 18.8 billion records were exposed year to date, a 32% decline compared to the 27.8 billion records leaked in the first half of 2020.
New DNS Vulnerability Allows 'Nation-State Level Spying' On Companies
Security researchers found a new class of DNS vulnerabilities impacting major DNS-as-a-Service (DNSaaS) providers that could allow attackers to access sensitive information from corporate networks.
DNSaaS providers (also known as managed DNS providers) provide DNS renting services to other organisations that do not want to manage and secure yet another network asset on their own.
These DNS flaws provide threat actors with nation-state intelligence harvesting capabilities with a simple domain registration.
Constant Review Of Third Party Security Critical As Ransomware Threat Climbs
Enterprises typically would give their third-party suppliers "the keys to their castle" after carrying out the usual checks on the vendor's track history and systems, according to a New York-based Forrester analyst who focuses on security and risk. They believed they had done their due diligence before establishing a relationship with the supplier, but they failed to understand that they should be conducting reviews on a regular basis, especially with their critical systems suppliers. Third-party suppliers should have the ability to deal with irregular activities in their systems and the appropriate security architecture in place to prevent any downstream effects, he added.
Kaseya Ransomware Attack Sets Off Race To Hack Service Providers
A ransomware attack in July that paralyzed as many as 1,500 organisations by compromising tech-management software from a company called Kaseya has set off a race among criminals looking for similar vulnerabilities, cyber security experts said. An affiliate of a top Russian-speaking ransomware gang known as REvil used two gaping flaws in software from Florida-based Kaseya to break into about 50 managed services providers (MSPs) that used its products, investigators said. Now that criminals see how powerful MSP attacks can be, "they are already busy, they have already moved on and we don’t know where," said head of the non-profit Dutch Institute for Vulnerability Disclosure, which warned Kaseya of the weaknesses before the attack.
‘It’s Quite Feasible To Start A War’: Just How Dangerous Are Ransomware Hackers?
Secretive gangs are hacking the computers of governments, firms, even hospitals, and demanding huge sums. But if we pay these ransoms, are we creating a ticking time bomb? They have the sort of names that only teenage boys or aspiring Bond villains would dream up (REvil, Grief, Wizard Spider, Ragnar), they base themselves in countries that do not cooperate with international law enforcement and they don’t care whether they attack a hospital or a multinational corporation. Ransomware gangs are suddenly everywhere, seemingly unstoppable – and very successful.
Joint UK/US Advisory Detailing Top 30 Vulnerabilities Include Plenty Of Usual Suspects
A joint advisory from law enforcement agencies in the US, UK, and Australia this week tallied the 30 most-frequently exploited vulnerabilities. Perhaps not surprisingly, the list includes a preponderance of flaws that were disclosed years ago; everything on the list has a patch available for whoever wants to install it. But as we've written about time and again, many companies are slow to push updates through for all kinds of reasons, whether it's a matter of resources, know-how, or an unwillingness to accommodate the downtime often necessary for a software refresh. Given how many of these vulnerabilities can cause remote code execution—you don't want this—hopefully they'll start to make patching more of a priority.
https://www.wired.com/story/top-vulnerabilities-russia-nso-group-iran-security-news/
Average Total Cost Of A Data Breach Increased By Nearly 10% Year Over Year
Based on in-depth analysis of real-world data breaches experienced by over 500 organisations, the global study suggests that security incidents became more costly and harder to contain due to drastic operational shifts during the pandemic, with costs rising 10% compared to the prior year. Businesses were forced to quickly adapt their technology approaches last year, with many companies encouraging or requiring employees to work from home, and 60% of organisations moving further into cloud-based activities during the pandemic. The new findings suggest that security may have lagged behind these rapid IT changes, hindering organizations’ ability to respond to data breaches.
https://www.helpnetsecurity.com/2021/07/29/total-cost-data-breach/
65% Of All DDoS Attacks Target US And UK
Distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks are common for cyber criminals who want to disrupt online-dependent businesses. According to the data analysed by a VPN team, 65% of all distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks are directed at the US or UK. Computers and the internet industry are the favourite among cyber criminals. The United States was a target for 35% of all DDoS attacks in June 2021. Cyber criminals launched DDoS attacks against Amazon Web Services, Google, and other prominent US-based companies in the past. The United Kingdom comes second as it fell victim to 29% of all DDoS attacks. As the UK has many huge businesses, they often are targeted by hackers for valuable data or even a ransom. China was threatened by 18% of all DDoS attacks in June 2021. Assaults from and to China happen primarily due to political reasons, to interrupt some government agency.
https://www.pcr-online.biz/2021/08/05/65-of-all-ddos-attacks-target-us-and-uk/
Threats
Ransomware
Ransomware Attacks Rise Despite US Call For Clampdown On Cyber Criminals
BlackMatter Ransomware Gang Rises From The Ashes Of DarkSide, Revil
Criminals Are Using Call Centres To Spread Ransomware In A Crafty Scheme
Phishing
Microsoft Warns Office 365 Users Over This Sneaky Phishing Campaign
Spear Phishing Now Targets Employees Outside The Finance And Executive Teams, Report Says
Other Social Engineering
Malware
A Wide Range Of Cyber Attacks Leveraging Prometheus TDS Malware Service
Several Malware Families Targeting IIS Web Servers With Malicious Modules
Microsoft: This Windows And Linux Malware Does Everything It Can To Stay On Your Network
Mobile
An Explosive Spyware Report Shows Limits Of IOS, Android Security
This Android Malware Steals Your Data In The Most Devious Way
The Latest Android Bank-Fraud Malware Uses A Clever Tactic To Steal Credentials
Vulnerabilities
Code Execution Flaw Found In Cisco Firepower Device Manager On-Box Software
Cisco Issues Critical Security Patches To Fix Small Business VPN Router Bugs
Decade-Long Vulnerability In Multiple Routers Could Allow Network Compromise
Security Researchers Warn Of TCP/IP Stack Flaws In Operational Technology Devices
PwnedPiper PTS Security Flaws Threaten 80% of Hospitals In The U.S.
Data Breaches
Threat Actors Leaked Data Stolen From EA, Including FIFA Code
Hackers Breach San Diego Hospital, Gaining Access To Patients'... Well, Uh, Everything
OT, ICS, IIoT and SCADA
Organised Crime & Criminal Actors
Cryptocurrency/Cryptojacking
Supply Chain
Nation State Actors
Here's 30 Servers Russian Intelligence Uses To Fling Malware At The West, Beams RiskIQ
Russian Federal Agencies Were Attacked With Chinese Webdav-O Virus
New Chinese Spyware Being Used In Widespread Cyber Espionage Attacks
Suspected Chinese Hackers Took Advantage Of Microsoft Exchange Vulnerability To Steal Call Records
Iranian APT Lures Defense Contractor In Catfishing-Malware Scam
Chinese Hackers Target Major Southeast Asian Telecom Companies
Cloud
Reports Published in the Last Week
Other News
Leaked Document Says Google Fired Dozens Of Employees For Data Misuse
Hybrid Work Is Here To Stay – But What Does That Mean For Cyber Security?
Huawei To America: You're Not Taking Cyber Security Seriously Until You Let China Vouch For Us
Trusted Platform Module Security Defeated In 30 Minutes, No Soldering Required
Credit-Card-Stealing, Backdoored Packages Found In Python's PyPi Library Hub
As usual, contact us to help assess where your risks lie and to ensure you are doing all you can do to keep you and your business secure.
Look out for our weekly ‘Cyber Tip Tuesday’ video blog and on our YouTube channel.
You can also follow us on Facebook, Twitter and LinkedIn.
Links to articles are for interest and awareness and linking to or reposting external content does not endorse any service or product, likewise we are not responsible for the security of external links.
Cyber Weekly Flash Briefing 25 September 2020: GFSC consult on new Cyber Rules; FinCEN leak exposes poor data security; Zerologon attacks detected; ransomware gang behind German hospital death
Cyber Weekly Flash Briefing 25 September 2020: GFSC consulting on new Cyber Rules; Leaked FinCEN files expose poor data security; Microsoft detects active Zerologon attacks; ransomware crew fingered for German hospital death; malware that steals your most sensitive data on the rise; Ransomware is evolving; top threats inside malicious emails; Credential Stuffing behind Recent Attacks
Links to articles are for interest and awareness and linking to or reposting external content does not endorse any service or product, likewise we are not responsible for the security of external links.
GFSC new Cyber Rules and Guidance out for consultation
The GFSC have put the Cyber Security Rules and Guidance Consultation Paper up on their website and consultation hub.
Why this matters:
The new rules and accompanying guidance came out of the 18 month thematic review which ended last year, which found that regulated financial service firms within the Bailiwick of Guernsey were not taking risks from cyber threats seriously enough and were lacking in appropriate protections and controls. These new rules seek to rectify this but many firms on the Island are going to have to do work to become compliant, especially around their ability to monitor for and detect unusual activity that could be indicative of a actual or attempted intrusion or breach.
The rules and guidance can be found here:
Leaked FinCEN files expose poor data security
Leaked documents, dubbed the “FinCEN Files,” describe global money laundering of $2 trillion processed by many of the world’s biggest banks between 2000 and 2017. The reveal illuminates the struggle for the financial industry and government to provide ironclad data protection.
“This sensational and unprecedented leak clearly demonstrates a wide spectrum of data protection weaknesses in the governmental sector, affecting even the most developed Western countries,” Ilia Kolochenko, founder and CEO of ImmuniWeb, said of the files.
“From a cybersecurity standpoint, we may expect a growing lack of trust to governmental agencies, which on one side have quasi-unlimited access to the most sensitive data of the largest organisations, while cannot duly safeguard this data on the other side,” he said.
The latest disclosure exposing apparently insufficient attempts by the public and private sectors to curb corruption came to light in a BuzzFeed News report which detailed more than 2,500 reported cases, including 2,100 Suspicious Activity Reports (SAR) filed by financial institutions with the U.S. Treasury Department’s Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN).
JPMorgan Chase, Citigroup, Bank of America, Deutsche Bank, HSBC and Standard Chartered are among the financial institutions cited in the leaked files as processing dirty money around the world. The documents may have come from a whistleblower or insider at FinCEN. The International Consortium of Investigative Journalists (ICIJ), which represents 108 news organizations in 88 countries, is conducting a probe of the matter.
Why this matters:
Other similar investigative reports on similar wrongdoing focused single financial, tax or legal institutions, such as the 2017 Panama Papers emanating from clients of the law firm Mossack Fonseca. But the FinCEN docs reveal that a wide array of people from oligarchs and corrupt politicians to drug dealers and organised crime throughout the world know how to circumvent the system’s supposed checks and balances.
Read more: https://www.scmagazine.com/home/security-news/leaked-fincen-files-expose-poor-data-security/
Microsoft says it detected active attacks leveraging Zerologon vulnerability
Hackers are actively exploiting the Zerologon vulnerability in real-world attacks, Microsoft's security intelligence team said this week.
The attacks were expected to happen, according to security industry experts.
Multiple versions of weaponized proof-of-concept exploit code have been published online in freely downloadable form since details about the Zerologon vulnerability were revealed a week ago.
The first proof-of-concept exploit was published hours after the explanatory blog post, confirming initial analysis that the Zerologon bug is easy to exploit, even by low-skilled threat actors.
Why this matters:
Put simply the Zerologon bug is a vulnerability in Netlogon, the protocol used by Windows systems to authenticate against a Windows Server running as a domain controller. Exploiting the Zerologon bug can allow hackers to take over the domain controller, and inherently a company's internal network.
Zerologon was described by many as the most dangerous bug revealed this year. US federal agencies were given three days to patch domain controllers or disconnect them from federal networks.
As several security experts have recommended since Microsoft revealed the attacks, companies that have their domain controller exposed on the internet should take systems offline to patch them.
These internet-reachable servers are particularly vulnerable as attacks can be mounted directly, without the hacker first needing a foothold on internal systems.
Doppelpaymer ransomware crew fingered for attack on German hospital that caused death of a patient
The Doppelpaymer ransomware gang were behind the cyber-attack on a German hospital that led to one patient's death, according to local sources.
A German newspaper carried a report that Doppelpaymer's eponymous ransomware had been introduced to the University Hospital Düsseldorf's network through a vulnerable Citrix product.
That ransomware infection, activated last week, is said by local prosecutors to have led to the death of one patient who the hospital was unable to treat on arrival. She died in an ambulance while being transported to another medical facility with functioning systems.
Why this matters:
According to a report handed to the provincial government of North Rhine-Westphalia and seen by the German Press Association (DPA), the ransomware's loader had been lurking on the hospital's network since December 2019, the same month a patch was issued by Citrix for CVE-2019-19781 – the same vuln exploited to hit the hospital.
Whilst this is the first time a loss of life has been directly attributed to ransomware the threats are increasing all the time.
Vulnerabilities must be patched as soon as possible to stop known vulnerabilities from being used in attacks.
Read more: https://www.theregister.com/2020/09/23/doppelpaymer_german_hospital_ransomware/
“LokiBot,” the malware that steals your most sensitive data, is on the rise
Agencies in the US have reported seeing a big uptick in infections coming from LokiBot, an open source DIY malware package for Windows that’s openly sold or traded for free in underground forums. It steals passwords and cryptocurrency wallets, and it can also download and install new malware.
The increase was measured by an automated intrusion-detection system for collecting, correlating, analysing, and sharing computer security information.
US cyber agency CISA observed a notable increase in the use of LokiBot malware by malicious cyber actors since July 2020 according to an alert issued this week.
Why this matters:
While not quite as prevalent or noxious as the Emotet malware, LokiBot remains a serious and widespread menace. The infostealer spreads through a variety of methods, including malicious email attachments, exploitation of software vulnerabilities, and trojans sneaked into pirated or free apps. Its simple interface and reliable codebase make it attractive to a wide range of crooks, including those who are new to cybercrime and have few technical skills.
Ransomware is evolving, but the key to preventing attacks remains the same
Ransomware attacks are getting more aggressive according to a senior figure at Europe's law enforcement agency, but there are simple steps which organisations can follow to protect themselves – and their employees – from falling victim to attacks.
"Ransomware is one of the main threats," said the head of operations at Europol's European Cybercrime Centre (EC3). Europol supports the 27 EU member states in their fight against terrorism, cybercrime and other serious and organised forms of crime.
"Criminals behind ransomware attacks are adapting their attack vectors, they're more aggressive than in the past – they're not only encrypting the files, they're also exfiltrating data and making it available," he explained. "From a law enforcement perspective, we have been monitoring this evolution."
Why this matters:
This year has seen a rise in ransomware attacks where cyber criminals aren't just encrypting the networks of victims and demanding six-figure bitcoin payment to return the files, but they're also threatening to publish sensitive corporate information and other stolen data if the victim doesn't pay the ransom.
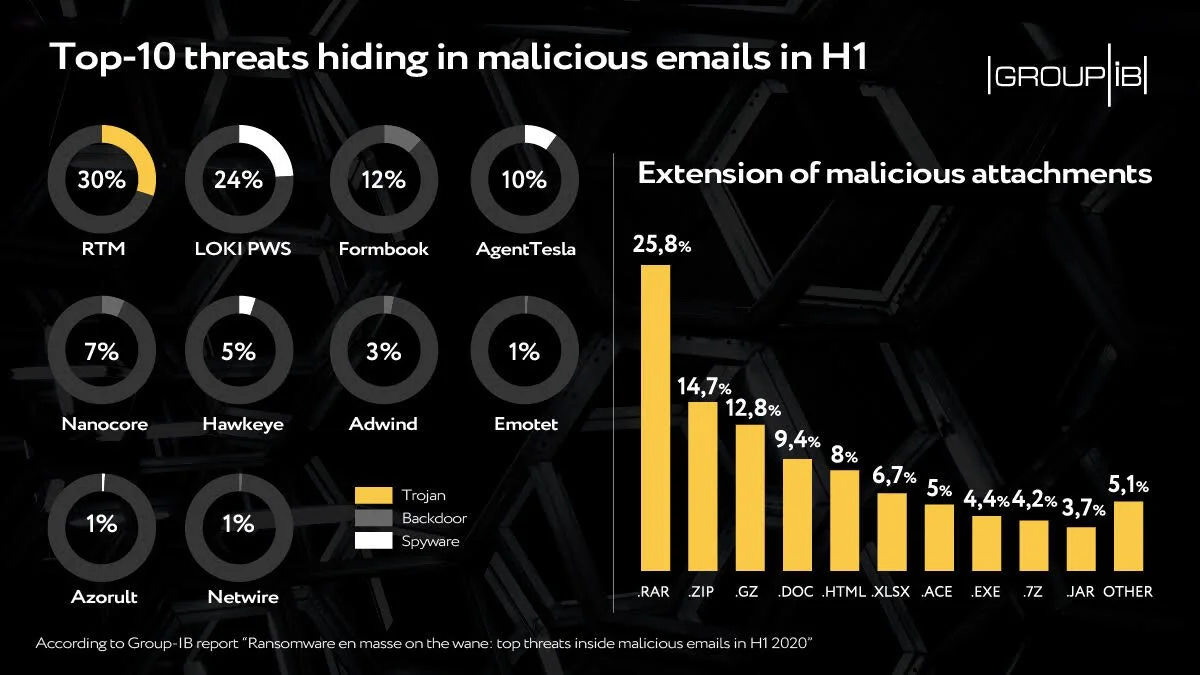
A look at the top threats inside malicious emails
Web-phishing targeting various online services almost doubled during the COVID-19 pandemic: it accounted for 46 percent of the total number of fake web pages, Group-IB reveals.
Ransomware, the headliner of the previous half-year, walked off stage: only 1 percent of emails analysed contained this kind of malware. Every third email, meanwhile, contained spyware, which is used by threat actors to steal payment data or other sensitive info to then put it on sale in the darknet or blackmail its owner.
Downloaders, intended for the installation of additional malware, and backdoors, granting cybercriminals remote access to victims’ computers, also made it to top-3. They are followed by banking Trojans, whose share in the total amount of malicious attachments showed growth for the first time in a while.
According to the data, in H1 2020 detected malicious emails were:
43 percent of the malicious mails had attachments with spyware or links leading to their downloading
17 percent contained downloaders
16 percent had backdoors
15 percent had banking trojans
Ransomware, which in the second half of 2019 hid in every second malicious email, almost disappeared from the mailboxes in the first six months of this year with a share of less than 1 percent.
Why this matters:
These findings confirm adversaries’ growing interest in Big Game Hunting. Ransomware operators have switched from attacks en masse on individuals to corporate networks. Thus, when attacking large companies, instead of infecting the computer of a separate individual immediately after the compromise, attackers use the infected machine to move laterally in the network, escalate the privileges in the system and distribute ransomware on as many hosts as possible.
Read more: https://www.helpnetsecurity.com/2020/09/21/top-threats-inside-malicious-emails/
Credential Stuffing: the Culprit of Recent Attacks
A year ago, researchers found that 2.2 billion leaked records, known as Collection 1-5, were being passed around by hackers. This ‘mega leak’ included 1.2 billion unique email addresses and password combinations, 773 million unique email addresses and 21 million plaintext passwords. With this treasure trove, hackers can simply test email and password combinations on different sites, hoping that a user has reused one. This popular technique is known as credential stuffing and is the culprit of many recent data breaches.
There are only a few months left of 2020 but this year has seen its fair share of major data breaches including:
Marriott International experienced another mega breach, when it was still recovering from the 2018 data breach that exposed approximately 339 million customer records
Zoom became a new favourite for hackers due to the remote working mandated in many parts of the world - in early April Zoom fell victim to a credential stuffing attack, which resulted in 500,000 of Zoom’s usernames and passwords being exposed on the Dark Web.
GoDaddy, the world’s largest domain registrar confirmed in April that credentials of 28,000 of its customer web hosting accounts were compromised in a security incident back in October 2019.
Nintendo - in March, users reported unauthorised logins to their accounts and charges for digital items without their permission. In June Nintendo advised that approximately 300,000 accounts were affected by the breach, resulting in the compromise of personal identifiable information such as email address, date of birth, country and gender.
Why this matters:
It has become evident that many of the recent data breaches were the result of credential stuffing attacks leveraging compromised passwords or passphrases. Credential stuffing attacks are automated hacks where stolen usernames and password combinations are thrown at the login process of various websites in an effort to break in. With billions of compromised credentials already circulating the Dark Web, credential stuffing attacks can be carried out with relative ease and with a 1-3% success rate.
When the account of an employee is compromised, hackers can gain access to sensitive data that organisation has collected, and sell it on the Dark Web. The stolen data, often including login credentials, can then be used to infiltrate other organisations’ systems which creates a never-ending cycle.
This is why the LinkedIn breach was blamed for several secondary compromises due to users recycling their exposed LinkedIn passwords on other sites.
Read more: https://www.infosecurity-magazine.com/blogs/credential-stuffing-recent-attacks/